Understanding Double Girder Bridge Cranes
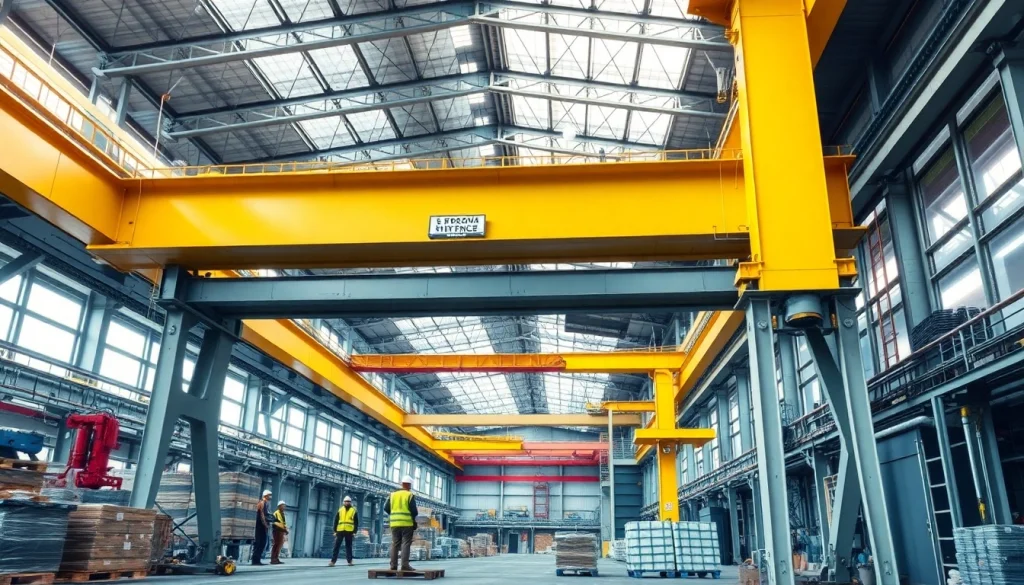
Double girder bridge cranes are a vital component in the material handling domain, providing enhanced stability and lifting capabilities compared to their single girder counterparts. These cranes consist of two parallel girders, ensuring that heavy loads can be managed efficiently across extensive spans. When exploring options, a double girder bridge crane offers versatility in various applications, making it a crucial investment for manufacturing and logistical industries.
What is a Double Girder Bridge Crane?
A double girder bridge crane is an overhead lifting system that features two main girders connected by a bridge, offering robust structures capable of supporting significant loads. This design is optimal for heavy-duty applications, as it efficiently distributes weight and enhances stability. The hoist is typically suspended from the upper flanges, allowing for maximum hook height and versatile operation. This crane type is especially favored in environments that demand high lifting capacities and precision, functioning seamlessly in various industrial settings.
Components and Design Features
The design of a double girder bridge crane includes several essential components:
- Main Girders: The two primary girders form the backbone of the crane, designed to carry heavy loads with excellent resistance to bending and deformation.
- End Trucks: Situating at either end of the girder system, these components allow the crane to move along the runway tracks, enhancing its mobility.
- Hoist: This lifting mechanism is pivotal for raising and lowering loads. It can be electric or manual, depending on specific operational demands.
- Cross Travel Mechanism: This feature enables lateral movement across the girder, facilitating precise placement of materials.
- Control System: Most modern double girder cranes are equipped with advanced control systems, including wireless options for improved operator convenience and safety.
Benefits Over Single Girder Cranes
Double girder cranes offer numerous advantages when compared to single girder designs:
- Higher Load Capacity: Capable of lifting heavier loads, double girder cranes can typically handle weights exceeding 20 tons, making them suitable for industrial applications involving large machinery or heavy components.
- Greater Span: These cranes can traverse wider spans, often up to 150 feet, providing flexibility in installation and operation.
- Increased Hook Height: The configuration allows for a higher hook position, maximizing vertical lift and load handling efficiency.
- Stability: The dual girder design ensures greater stability, minimizing sway during operation and reducing the risk of accidents.
Applications of Double Girder Bridge Cranes
Industries Utilizing Double Girder Cranes
Double girder bridge cranes find applications across a multitude of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Heavy manufacturing facilities utilize these cranes for assembly line operations, where precision and weight handling are critical.
- Aerospace: The aerospace sector requires demanding lifting capabilities for components and equipment, where double girder cranes excel.
- Construction: In construction sites, these cranes facilitate the movement of heavy materials such as steel beams and pre-cast concrete components.
- Shipping and Logistics: Warehouses and shipping ports implement these cranes to manage heavy loads effectively, optimizing cargo handling and storage.
Optimal Settings for Installation
The installation of double girder bridge cranes is ideal in settings where:
- Heavy loads are routinely lifted, necessitating robust support systems.
- Wider spans between supports are required to allow for unobstructed floor space.
- High lift heights are needed to maximize operational efficiency.
- Precision in load placement is crucial, particularly in assembly or packaging lines.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Several organizations have successfully integrated double girder bridge cranes into their operations:
- ABC Manufacturing: Implemented a double girder crane that increased operational efficiency by 30% by allowing simultaneous lifting of multiple components.
- XZY Logistics: Utilized double girder cranes for enhanced cargo handling, resulting in a 25% reduction in turnaround time for shipments.
- LMN Construction: Adopted these cranes for heavy lifting at large project sites, improving safety and reducing incidences of equipment failure.
Choosing the Right Double Girder Bridge Crane
Key Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate double girder bridge crane involves careful consideration:
- Load Requirements: Determine the maximum weight that needs to be lifted regularly, as this will dictate the crane’s specifications.
- Span Distance: Assess the distance between support columns; the crane must be able to cover this span without compromising safety or efficiency.
- Height Limitations: Address any height restrictions on the installation site, ensuring the crane can be installed without obstructions.
- Frequency of Use: Consider how often the crane will be in operation to ensure it meets the required lifecycle and durability standards.
Evaluating Load Capacity and Span
When evaluating load capacity and span, it’s vital to consider the following:
- The crane’s capacity should exceed the maximum load by a margin to accommodate dynamic loads and prevent overloading.
- Consult manufacturer specifications to ensure that the crane can handle the span without flexing or bending, which could lead to failure.
Common Misconceptions About Selection
There are several misconceptions surrounding the selection of double girder cranes:
- All Cranes are the Same: Different configurations serve various purposes; understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimal functionality.
- Cost is the Only Factor: While price is important, operational performance, safety features, and maintenance should also influence decisions.
- Single Girder Cranes are Always Cheaper: Although they may have lower upfront costs, single girder cranes can incur higher operational costs and reduced efficiency.
Maintenance and Safety Best Practices
Routine Maintenance Checks
An effective maintenance regime is crucial for the longevity and safe operation of double girder cranes. It typically involves:
- Regular inspections of all mechanical components, including the hoist, trolley wheels, and electrical systems.
- Lubrication of moving parts to prevent wear and tear.
- Checking for signs of corrosion or structural damage, particularly on the girders and frames.
- Testing safety devices regularly to ensure they operate as intended.
Safety Protocols for Operators
Ensuring safety in the operation of double girder bridge cranes is paramount. Operators should:
- Receive comprehensive training on crane operation and safety protocols.
- Adhere to load capacity limits and utilize appropriate signals and communication methods.
- Wear necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) while operating or working in proximity to cranes.
- Conduct daily checks before operation to identify any potential issues.
Addressing Common Operational Challenges
Crane operators often face various operational challenges. Effective strategies include:
- Implementing a systematic maintenance schedule to reduce unexpected breakdowns.
- Using technology such as load monitoring systems to prevent overload situations.
- Fostering a culture of safety to promote adherence to protocols and responsiveness to hazards.
Future Trends in Double Girder Bridge Crane Technology
Emerging Technologies in Crane Design
The future of double girder bridge cranes is poised for significant advancements through technological innovations, including:
- Smart Crane Technology: Integrating IoT devices for real-time monitoring of crane conditions and load capacities.
- Lightweight Materials: Utilizing advanced materials that enhance strength while reducing overall weight, leading to more efficient operations.
- Advanced Controls: Introducing more intuitive control systems, including voice-activated commands and augmented reality interfaces.
Impact of Automation on Crane Operations
Automation is increasingly becoming a critical component in crane operations, with implications such as:
- Increased efficiency in material handling, significantly reducing labor costs.
- Enhanced precision in lifting and placement, minimizing human error.
- Remote operation capabilities, allowing for safer management of operations in hazardous environments.
Predictions for 2025 and Beyond
As we look towards 2025, several key predictions emerge for the future of double girder bridge cranes:
- The integration of AI for predictive maintenance, allowing for proactive rather than reactive servicing.
- Greater emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, aligning with global environmental goals.
- Enhanced connectivity with other automated systems in manufacturing and logistics, creating a more integrated approach to material handling.